Table of Contents
Global Surface Settings
Properties in this category allow you to customize scene surfaces globally, meaning changing any property here will affect the entire scene unless the object's materials use a property override.
Enable Coverage
Enables coverage in materials that use Weatherade shaders. If disabled, then the shaders will act like Unity Standard shadar.
Basic Settings
Paintable Coverage
This option enables the ability to edit the automatically generated coverage occlusion mask. Vertex colors are used for regular MeshRenderes, and Terrains use an additional texture-mask. Both can be painted with Total Brush which is included in the package. In BiRP currenty only ⠀R⠀ channel is used. In URP all 4 channels can be utilized, if different snow layers are used.
Use Average Normals
If this option is enabled, the shader will use an additional set of normals stored in the UV4 channel. This helps eliminate mesh “cracks” when using displacement and improves the coverage on meshes with split normals.

Generate these normals by selecting an object in the scene and clicking the “Average Normals” button in its material UI, or go to the Total Brush window and click the same button there.
Stochastic Sampling
Enables stochastic sampling that eliminates visible tiling artifacts. This option has a performance overhead because the texture fetch operation is performed 3 times instead of 1.

Coverage Texture
Texture which is used to build the snow coverage surface.
It uses a specific channel mapping:
- Normals - ⠀R⠀ ⠀G⠀ - adds pseudo-relief details to the snow.
- Height - ⠀B⠀ - used for the displacement feature and as a snow surface mask on the coverage transitions, to make them more organic.
- Smoothness - ⠀A⠀ - used for the snow surface glossiness. Can be also reused for the Sparkle effect.
- Texture Type: Default
- sRGB: disabled
All other settings can be left as default.
Tiling
The uniform tiling value of the Coverage Texture.
Color
Color of the coverage.
Smoothness (URP only)
Coverage smoothness range. Remaps the Coverage Texture alpha channel, which is used as smoothness.
Normal Scale
Bumpiness of the coverage. The ⠀R⠀ and ⠀G⠀ channels of the Coverage Texture are used to construct normals.
Amount
Amount of the сoverage applied to the surface.
Triplanar Blend Hardness (URP only)
Blend hardness between the triplanar projections.
Emission Masking
Masks the base surface emission effect by the coverage.

Coverage Normals Overlay
Forces to overlay coverage normals over the base surface normals even when Displacement is disabled. This value is a linear interpolation between the base normal map and the coverage normal map.
DETAIL MAP (URP only)
Detail map can help to improve the snow surface details close to the camera.

Detail Texture
Texture used for the detail mapping. Channel mapping used:
- Normals - ⠀R⠀ ⠀G⠀ - adds additional micro-relief details to the snow.
- Smoothness - ⠀B⠀ - used for the snow surface glossiness and Color Enhance.
- Texture Type: Default
- sRGB: disabled
All other settings can be left as default.
Tiling
Tiling of the Detail Texture.
Remap
Remap the Detail Texture ⠀B⠀ channel, which is used for the smoothness/Color Enhance.
Normal Scale
Micro-relief scale of the details.
Distance
The distance in units where the details will fade out.
AREA MASK
Area mask settings allow you to control how the coverage occlusion will look. All parameters here are related to each other.
Mask Range
Range of the coverage mask values. A value of 1 means the transitions between the coverage and base surfaces are as soft and wide as possible.
Bias
The bias of the coverage area.
This property is needed for two things:
- Fix the coverage banding and Z-clipping artifacts
- Shrink/expand the coverage occlusion mask in conjunction with the Mask Range.
Internally it works similar to the shadow bias property on the Unity light sources.

Leak Reduction
Reducing coverage leaks at the cost of increasing mask hardness.
Direction Offset
The linear offset from the original direction of the coverage instance. Values below 0 will create a stronger direction-dependent coverage mask, and values greater 0 can help add more coverage on the opposite side of the direction of the coverage instance. Internaly it just adds this value to the coverage direction mask.
On the examples below the coverage instance transform direction is set straight down:

Direction Range
Shrink/expand the coverage direction mask gradient. You can make the direction mask more hard lowering the range.
TESSELLATION
Improves the appearance of a surface when using the Displacement feature by subdividing the mesh triangles.
Weatherade implements the Edge Length tessellation method with some specific additions, that improves performance:
- View frustum culling (useful for large meshes such as terrain)
- Mask tessellation by snowdrift slopes
- Data-driven tessellation factor (works with Traces feature)
Example of the data-driven tessellation in action:

Edge Length
Maximum screen-space length of the edge. Edges longer than this value will be subdivided.
Snow Factor
Multiplier for the overall snow surface tessellation.
Snowdrift Range
Range of mask that used to increase the tessellation factor on snowdrift slopes.
Frustum Culling Offset
Maximum distance from camera's clip planes on which tessellation should not be applied.
Weatherade tessellation uses Frustum Culling to improve performance on large meshes by appling tessellation only for visible triangles. When Displacement is used you should increase this value to compensate the displacement and prevent mesh clipping. The higher the Coverage Displacement value, the larger this value should be. This can be especially noticable on a terrain mesh.

DISPLACEMENT
This feature allows you to raise the vertices of the mesh by the coverage mask, creating realistic snowdrifts.
Height Contrast
The contrast of the coverage height, when using the Displacement feature. For this purpose, the ⠀B⠀ channel of the Coverage Texture is used.
Heightmap LOD (URP only)
Defines the height map MIP level. Use higher values to get rid of noisy displacement.
Coverage Displacement
The amount of displacement added to the mesh verices. It depends on the Coverage Texture ⠀B⠀ channel, as it's used as a height map and multiplied by this value.
Offset
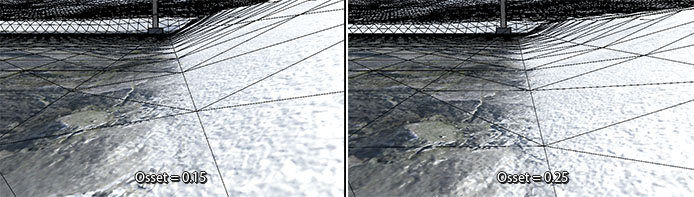
Offsets the black point of the coverage mask gradients. This useful to prevent unnecessary displacement on some not-covered areas.
See how the snowdrift's displacement starts too early and lifts the base surface when the Offset is too small:
TRACES
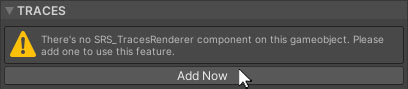
Enables interactive traces on the snow coverage.

If you haven't already added the Trace Mask Generator component, you will be prompted to do so. Click the “Add Now” button.
Base/Snow (URP only)
Blend factor between the base surface and coverage. If set to 0, the base texture will be visible inside the traces.
Color
Multiplier color of the generated traces. You can use it to simulate greater depth or ambient occlusion effects within a trace. If the color is set to white it will have no effect as it is internally multiplied by the coverage color.
Blend (Built-in RP only)
Factor of the linear blend between the coverage color and Color.
Range
Range of the trace mask, used for the color Blend. You can shrink this range to get sharper mask.
Normal Scale
The normal scale of the generated traces.
Use Detail Texture
Determines whether traces will use the global Detail Texture.
Detail Texture
The global texture, that used to add details to the generated traces.
It uses a specific channel mapping:
- Normals - ⠀R⠀ ⠀G⠀
- Height - ⠀B⠀
- Texture Type: Default
- sRGB: disabled
All other settings can be left as default.
Tiling
The uniform tiling of the Detail Texture.
Normal Scale
The normal scale of the details.
Detail Intensity
The intensity of the detail displacement, applied to the generated traces.
BLEND BY NORMALS
Tweaking properties here can help make coverage transitions more organic.

Strength
The amount of base surface normal map influence on the coverage transitions blending. Consider this like the well-known height blending technique, but without the need to provide an additional height map, since Weatherade simulates this using a normal map.
Power
Power of the normal map blending. This just raises the faked height map to a math power.
DISTANCE FADE
This feature allows you to eliminate the tiling artifacts on terrains by blending between original textures and LOD textures with lower tiling values.
Start Distance
The distance from camera at which the baked LOD texture starts to appear.
Folloff
The size of the fading gradient for the original/LOD texture. The higher the value, the softer the blend will be.
SPARKLE AND SSS
Sparkle effect adds these little shinny dots on the surface, which improves the snow appearens. SSS (SubSurface Scattering) simulates light penetration into the surface and exiting from different point.
SSS
Enables subsurface scattering effect on the snow.
Intensity
Intensity of the subsurface scattering effect.
Sparkle
Enables sparkle effect on the snow surface.

Mask
Optional black and white texture which ⠀R⠀ channel is used as a sparkle effect mask. If no texture is provided, the alpha channel of the main coverage texture can be used.
Amount
Amount of snow sparkle effect. This value depends on the Mask texture.
Brightness
Brightness of the snow sparkle effect.
Distance Fallow
Maximum draw distance of the sparkle effect. Decrease this value to prevent unwanted noise and artifacts on far distances.
Local-Space Mask Source
Source for the sparkle mask which will be used in the object local space.
LS Tiling
Uniform tiling of the local space mask.
Scree-Space Mask Source
Source for the sparkle mask which will be used in the screen space.
SS Tiling
Tiling of the screen-space mask.
Highlight Mask Expansion
Expansion of the highlight mask, that is used to show the sparkle effect only on highlights from the lights sources.
Lightmap Mask Power
Power of the lightmap mask. Values greater than 0 prevent the Sparkle and SSS effect in dark areas, when baked lighting is used.
Color Enhance (URP only)
Enhance the snow surface color. The Coverage Texture ⠀A⠀ + Detail Texture ⠀B⠀ channels are used as a source.
Highlight Brightness (URP only)
Brightness of the highlight from the main light.
SSS Remap (URP only)
Remap the SSS mask values. Coverage Texture ⠀A⠀ + Detail Texture ⠀B⠀ channels are used as a source.
Color Enhance Remap (URP only)
Remap the color enhance mask. Coverage Texture ⠀A⠀ + Detail Texture ⠀B⠀ channels are used as a source.